BluedragonKBT44
24.05.2021 •
Mathematics
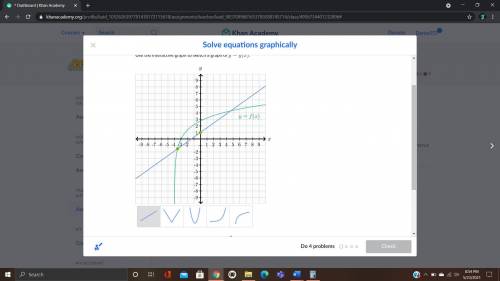
et f(x)=2\ln(x+4)f(x)=2ln(x+4)f, left parenthesis, x, right parenthesis, equals, 2, natural log, left parenthesis, x, plus, 4, right parenthesis and let g(x)=\dfrac23x+1g(x)= 3 2 x+1g, left parenthesis, x, right parenthesis, equals, start fraction, 2, divided by, 3, end fraction, x, plus, 1. The graph of y=f(x)y=f(x)y, equals, f, left parenthesis, x, right parenthesis is shown below. Use the interactive graph to sketch a graph of y=g(x)y=g(x)y, equals, g, left parenthesis, x, right parenthesis. LinearAbsolute_valueQuadraticExponentialLogarithm Let x_1x 1 x, start subscript, 1, end subscript and x_2x 2 x, start subscript, 2, end subscript be solutions of \,2\ln(x+4)=\dfrac23x+12ln(x+4)= 3 2 x+12, natural log, left parenthesis, x, plus, 4, right parenthesis, equals, start fraction, 2, divided by, 3, end fraction, x, plus, 1, where x_1
Solved
Show answers
More tips
- W Work and Career Everything You Need to Know About MBA Programs...
- S Sport How to Do Push-ups Correctly?...
- S Style and Beauty How to Grow Hair Faster: Real Methods and Advice...
- F Family and Home How to Remove Fading from Clothes: Tips and Tricks...
- F Food and Cooking How to Make Polendwitsa at Home?...
- F Family and Home Parents or Environment: Who Has the Most Influence on a Child s Upbringing?...
- P Philosophy Unbelievable stories of encounters with otherworldly forces...
- L Leisure and Entertainment How to Choose the Perfect Gift for Men on February 23rd?...
- H Health and Medicine How to Treat Whooping Cough in Children?...
- H Health and Medicine Simple Ways to Lower Cholesterol in the Blood: Tips and Tricks...
Answers on questions: Mathematics
- M Mathematics 4/x = 10/15 ( find the valie of x that will make the proportion true)...
- M Mathematics Prove the divisibility of the following numbers: 1. 25^7+5^13 by 30 2. 7^6+7^5−7^4 by 11 3. 5^5−5^4+5^3 by 7...
- M Mathematics When graphing a linear inequality, when can you not use (0, 0) as a test point to determine which side of a boundary line to shade? when the point (0, 0) is on the...
- M Mathematics Can you on 5, 6,7,8,9 and explain to me this will be 50 points...
- M Mathematics Triangle a: all sides have length 12 cm. triangle b: two sides have length 10 cm, and the included angle measures 60°. triangle c: base has length 15 cm, and base...
- M Mathematics Arecipe for sweet potato casserole calls for 3/4 cup of milk. martina has 6 cups of milk. how many sweet potato casseroles can she make with that amount?...
- M Mathematics What is the simplest form of /10,000x^64...
- M Mathematics Can someone me with this? i have no idea how to do this! make a scatter plot and draw a trend line for the data in the table. interpolate or extrapolate to estimate...
- M Mathematics Ascientist estimated that a mixture would need 6 milliliters of a chemical to balance. the actual amount needed was 7 milliliters. what was the percent error of...
- M Mathematics Nathan s lawn mower uses 23 of a tank of gas to cut three one-acre lawns. how many one-acre lawns can he cut with a full tank of gas? explain using ratios....

Ответ:
x=-3.5 , the points of the graph are 0,1 and 3,3
Step-by-step explanation:
Ответ:
The best estimate of the proportion of adults who say that the law goes easy on celebrities is 0.7435.
Step-by-step explanation:
Confidence interval concepts:
A confidence interval has two bounds, a lower bound and an upper bound.
A confidence interval is symmetric, which means that the point estimate used is the mid point between these two bounds, that is, the mean of the two bounds.
In this question:
CI is between 0.645 and 0.842. So the best estimate of the proportion is:
(0.645+0.842)/2 = 0.7435
The best estimate of the proportion of adults who say that the law goes easy on celebrities is 0.7435.