In a massive-star supernova explosion, a stellar core collapses to form a neutron star roughly 10 kilometers in radius. the gravitational potential energy released in such a collapse is approximately equal to g m2/r, where m is the mass of the neutron star, r is its radius, and g is the gravitational constant. using this formula, estimate the amount of gravitational potential energy released in a massive -star supernova explosion. how does it compare with the amount of energy radiated by the sun during its entire main-sequence lifetime?
Solved
Show answers
More tips
- C Computers and Internet Отправляем смс через интернет: легко и просто...
- H Health and Medicine Want to Lose Weight? Here s How Many Calories You Need Per Day...
- H Health and Medicine How Many Ribs Do Humans Have?...
- C Computers and Internet Dropbox: What is it and How to Use it...
- F Family and Home Choosing the Right Car Seat for Your Child: Tips and Recommendations...
- C Computers and Internet Е-head: How it Simplifies Life for Users?...
- A Auto and Moto How many blood alcohol level units are allowed in Russian traffic laws?...
- H Horoscopes, Magic, Divination Where Did Tarot Cards Come From?...
- H Health and Medicine How to Deal with Heat Stroke?...
- H Health and Medicine Sunstroke: Causes, Symptoms, and Precautions...
Answers on questions: Physics
- P Physics A person runs up 32 stairs of height 0.24 m. The person weighs 978.29 N. How much energy does it take for the person to reach the top of the stairs?...
- P Physics What is a non-economic benefit to international trade...
- P Physics Why is centrifugal force is a fake force?...
- P Physics Name 3 things you have in your home that you could use to make an electromagnet. NO LINKS OR FILES...
- P Physics A particle starts from rest and moves with a uniform acceleration of 5 m/s^2 for 10 seconds and then it moves with a constant velocity for 4 seconds. later it slows...
- P Physics Please help me thank you :)...
- P Physics Current Event Assignment Due today at 11:59 PM (Subject: P.E... Thank you) Instructions: Guidelines On How To Write A Current Events Essay A current events paper is...
- M Mathematics An ipod sold for $300, which was 200% of the actual cost.whst was the actual cost?...
- S Social Studies Read this sentence from the text chicago river: a reversal of fortunes....
- M Mathematics Hello can you me posted picture of question...

Ответ:
The concept used to solve this problem is gravitational potential Energy.
The equation is given by,
Where U is the gravitational potential energy
M is the mass of object
R is radius (10000m)
G is the unviersal gravitational constant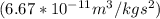
We know that the mass of neutron star is 1.4 times the mass of the sun.
It is known that the mass of sun is
Replacing the values in our equation we have:
Therefore the energy released in a massive-star supernova explosion is
To estimate the second point we know that the Total Energy by the Sun is
We can calculate the ratio between a supernova explosion and our entire main-sequence lifetime energy of the sun.
Therefore the amount of energy radiated by a supernova explosion is around times more than the entire main-sequence lifetime energy of the sun.
times more than the entire main-sequence lifetime energy of the sun.
Ответ:
in love with this song this is me all the time!
Explanation:
Be Happy,By; Dixie D'melio