sofiaisabelaguozdpez
28.05.2020 •
Physics
The rate at which a metal alloy oxidizes in an oxygen-containing atmosphere is a typical example of the practical utility of the Arrhenius equation. For example, the rate of oxidation of a magnesium alloy is represented by a rate constant, k. The value of k at 300°C is 1.05 * 10-8kg/(m4 # s). At 400°C, the value of k rises to 2.95 * 10-4kg/(m4 # s). Calculate the activation energy, Q, for this oxidation process (in units of kJ/mol).
Solved
Show answers
More tips
- O Other What happens if you get scared half to death twice?...
- F Family and Home What s That Noise When a Kettle Boils? The Science of Water and Steam...
- L Leisure and Entertainment History of International Women s Day: When Did the Celebration of March 8th Begin?...
- W Work and Career How much does an honest traffic police officer earn in a day?...
- F Food and Cooking Red Caviar: How to Choose the Best?...
- S Style and Beauty How to Get Rid of a Bruise: Tips and Tricks...
- H Health and Medicine Is Massage Necessary? Facts and Opinions...
- L Leisure and Entertainment Should You Buy a Ceramic Knife?...
- C Computers and Internet Best Antivirus: How to Choose Protection for Your Computer?...
- F Food and Cooking When is Easter in 2011?...
Answers on questions: Physics
- P Physics Distinguish between mass and momentum. Which is the measure of inertia and which is the measure of inertia in motion?...
- P Physics Two satellites with equal rest masses of 100 kg are traveling toward each other in deep space. one is traveling at 0.650c and the other at 0.850c. the satellites collide...
- P Physics Thomson is known for developing the plum pudding model of the atom. this is described as negative particles embedded in a gel of positive charge - much like raisins scattered...
- P Physics The united states consumes 2.5´1019 j of energy each year. a typical solar flare releases 5.0´1024 j of energy. how many years could we run the united states on the energy...
- P Physics The wheel on a vehicle has a rotational inertia of 2.0 kg*m^2. at the instant the wheel has a counterclockwise angular velocity of 6.0 rad/s, an average counterclockwise...
- P Physics What is the root word for organelle a. elle b. anelle c. org d. organ 12 points...
- P Physics Auniform brick of length 21 m is placed over the edge of a horizontal surface with a maximum overhang of 10.5 m attained without tipping. (picture one) now two identical...
- P Physics Objects a and b are brought close to each other. object a will soon become positively charged. identify the charge that must transfer for this situation to occur....
- E Engineering A Carnot heat engine receives heat from a reservoir at 900∘C at a rate of 800 kJ/min and rejects the waste heat to the ambient air at 27∘C. The entire work output of the...
- E English Read the excerpt from The Land. At first I just walked the grey, letting him get used to me. Then I bridled and saddled him and finally I mounted. I let him get accustomed...

Ответ:
The activation energy is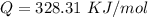
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The rate constant is k
at the temperature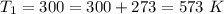
The value of k is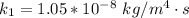
at temperature
The value of k is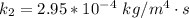
The rate constant is mathematically represented as
Where Q is the activation energy
R is the ideal gas constant with a value of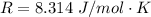
C is a constant
T is the temperature
For the first rate constant
For the second rate constant
Now the ratio between the two given rate constant is
=>![ln [\frac{k_1}{k_2} ] = \frac{Q}{R} * [\frac{1}{\frac{T_2 -1}{T_1} } ]](/tpl/images/0668/9767/33b26.png)
substituting values
=>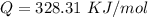
Ответ: